Non-surgical Rehabilitation
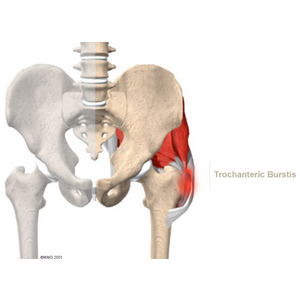
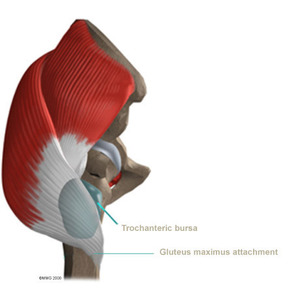
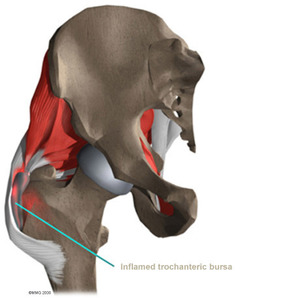
At Physio Med, treatment of trochanteric bursitis usually begins with simple measures used to calm inflammation, and may include heat or ice applications. Our Physiotherapists use hands on treatment and stretching to help restore your full hip range of motion. Improving strength and coordination in the buttock and hip muscles enables the femur to move in the socket smoothly and can help reduce friction on the bursa. Time required for recovery and rehabilitation varies for each patient, but as a guideline, you may expect to attend Physiotherapy sessions for four to six weeks before full motion and function return.
Younger patients who have this condition because of overuse can usually be treated by reducing their activities or changing the way they do their activities. Decreased activity, combined with our exercise Physiotherapy program of stretching and strengthening, and perhaps a brief course of anti-inflammatory medications, will usually resolve the problem. Patients may also want to consult with their Doctor or Pharmacist regarding the use of pain relief or anti-inflammatory medication.
Although the vast majority of our patients with trochanteric bursitis never require surgery, if you do, the Physiotherapists at Physio Med can provide a personalised post surgical Physiotherapy programme to help speed your recovery so that you can more quickly return to your active lifestyle.
Post-surgical Rehabilitation
If you have surgery, your hip will be bandaged with a well-padded dressing. Although the amount of Physiotherapy a patient needs relates to his or her own speed of recovery, as a general rule, you may expect to attend Physiotherapy sessions at Physio Med for up to two months after surgery.
Our first few treatment sessions will focus on controlling the pain and swelling after surgery. We will then have you begin exercises that gradually stretch and strengthen the muscles around the hip joint. Our physiotherapist will help you retrain these muscles to keep the ball of the femur moving smoothly in the socket. We will also provide you with tips on ways to do your activities without straining the hip joint.
At Physio Med, our goal is to help speed your recovery so that you can more quickly return to your everyday activities. When your recovery is well under way, regular visits to us will end. Although we will continue to be a resource, you will be in charge of doing your exercises as part of an ongoing home programme.
Portions of this document copyright MMG, LLC.